Guide to Create a Plugin
Guide to create a Plugin
Section titled “Guide to create a Plugin”Our commitment to the development of ArchiHUB as an open source project goes beyond the creation of the freely licensed tool. We also want to encourage contributions from ArchiHUB’s users, allowing anyone to extend ArchiHUB’s functionality by developing plugins. In this section, we will guide you through the process of creating a plugin for ArchiHUB.
What is a Plugin?
Section titled “What is a Plugin?”A plugin is an additional module that can be integrated into ArchiHUB to extend its functionality. Plugins can be used to add new features or even integrate ArchiHUB with other tools and services.
As an example, we have the plugin for audio and video transcription that allows users to automatically transcribe the content of their media files using OpenAI’s Whisper model.
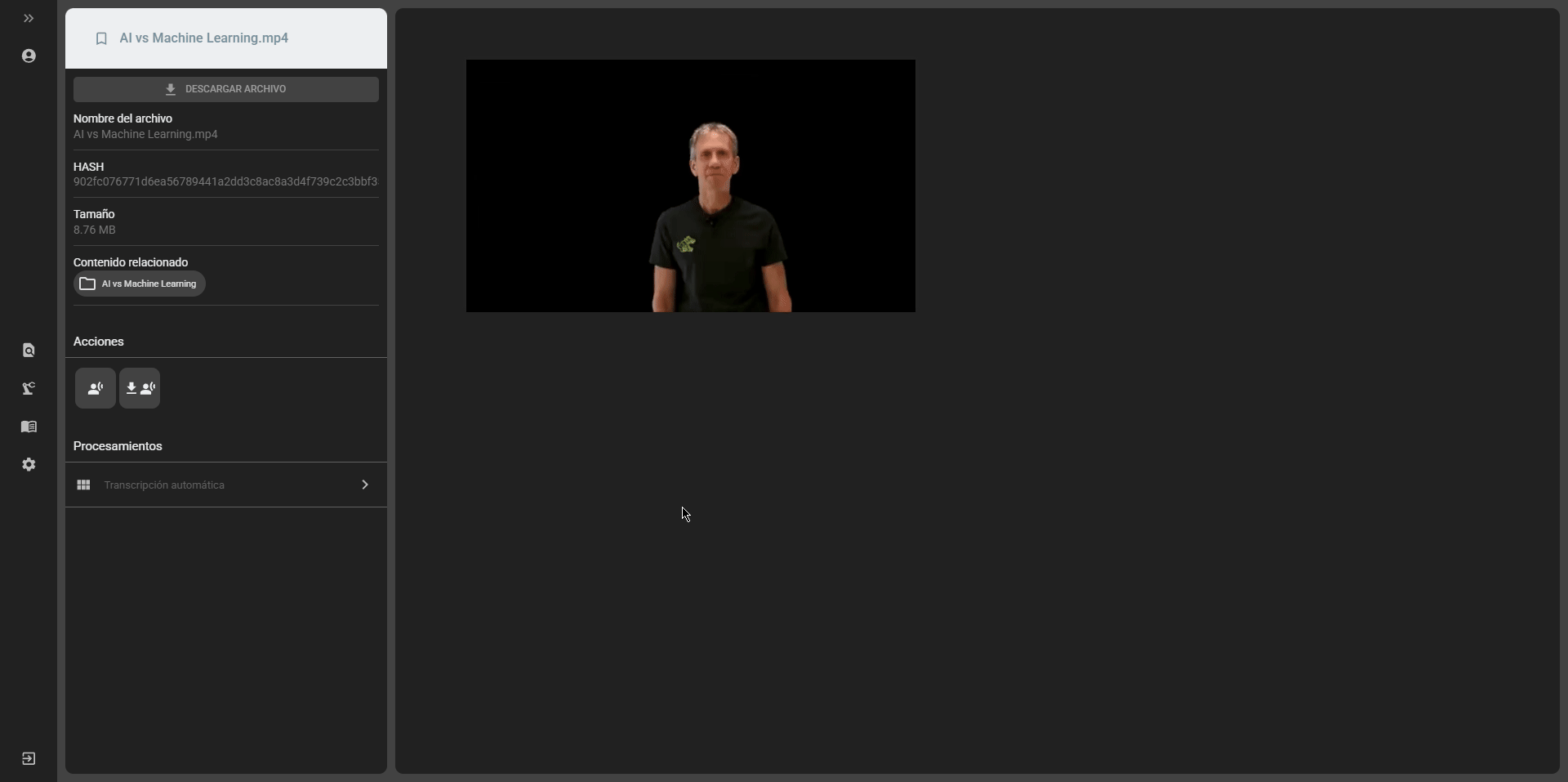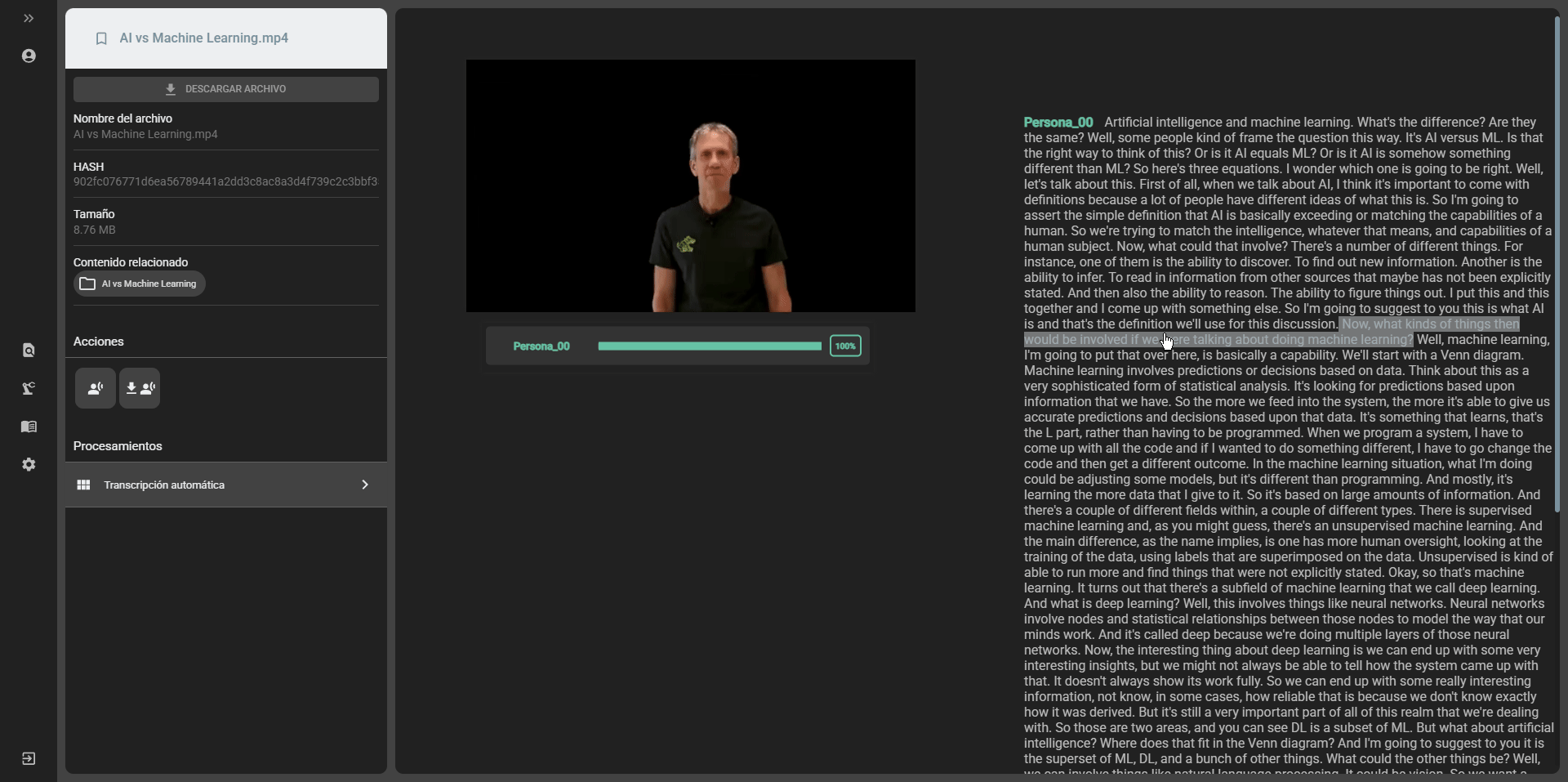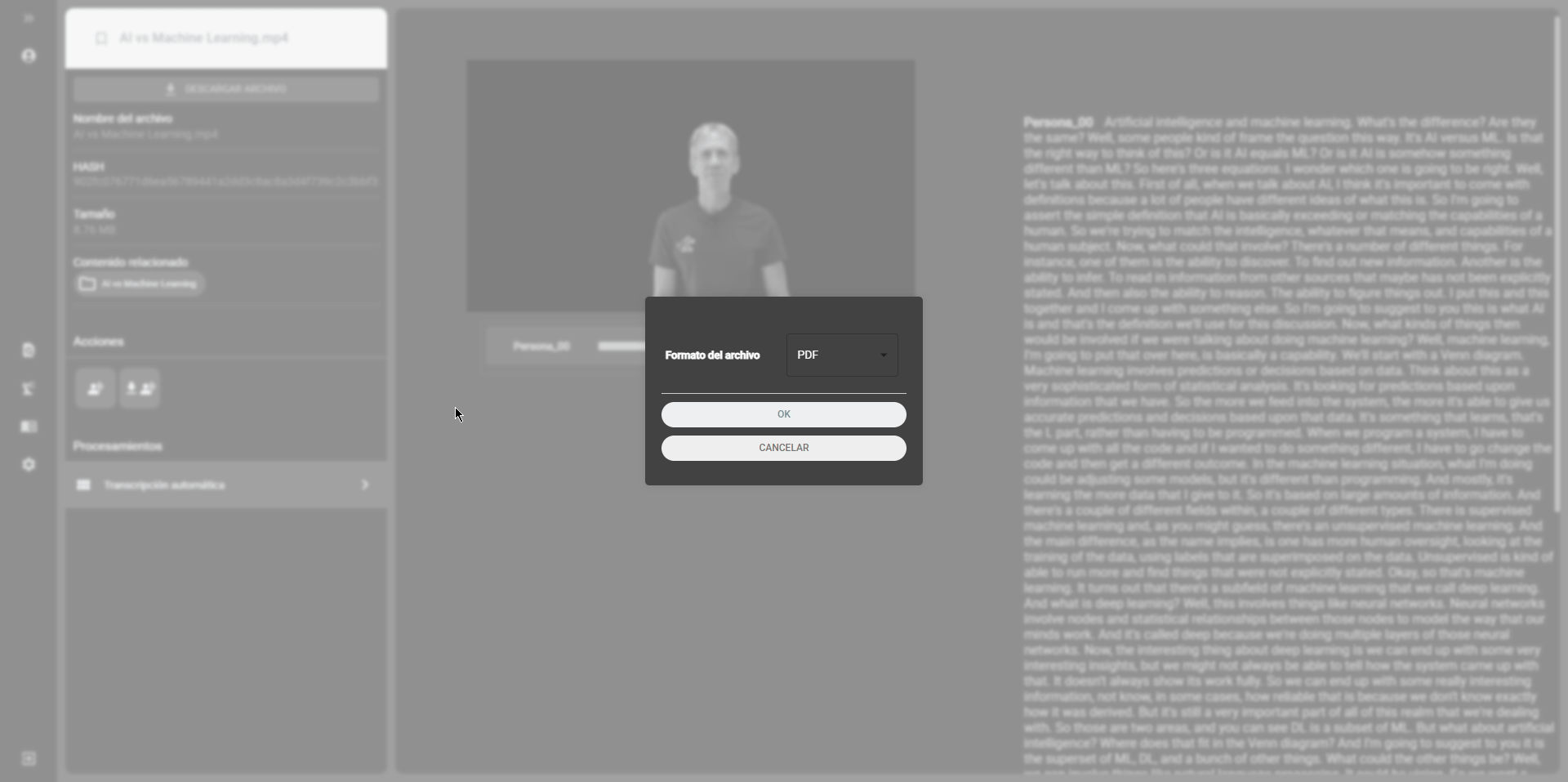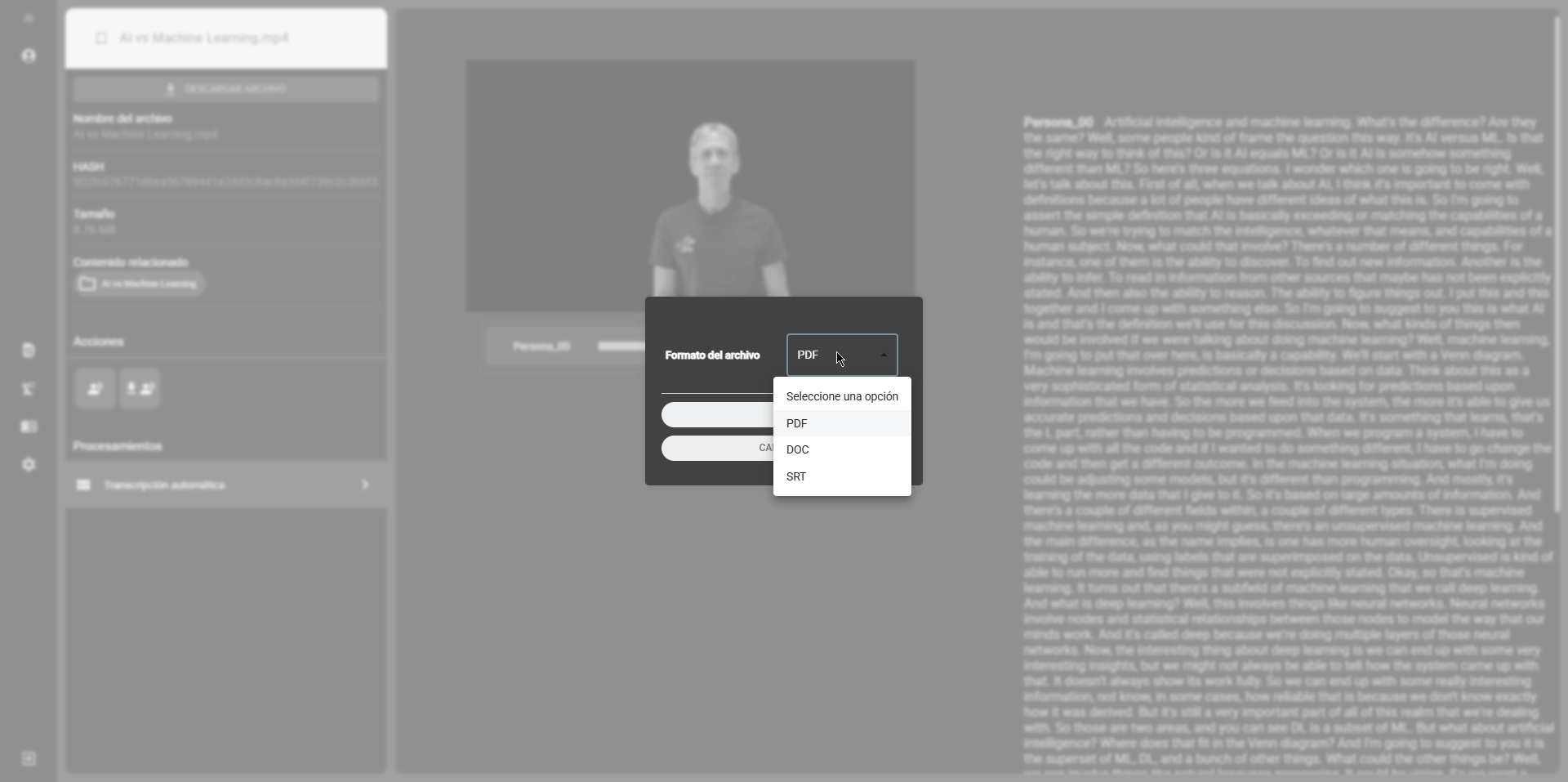
In this guide we are going to develop a plugin that allows the integration of ArchiHUB with the OpenAI API. This plugin will allow ArchiHUB users to modify resource titles using artificial intelligence.
Plugin structure
Section titled “Plugin structure”As a starting point, we will use the plugin template found in the ArchiHUB repository. This template contains the basic structure of a plugin and some examples of how different functionalities can be implemented. To access the template, you can clone the backend repository and look for the Plugin.py file in the app/utils/templates/ folder.
Plugins in ArchiHUB always contain the following parts:
- Structured plugin information: contains the basic plugin information. This is defined in JSON format and is located at the end of the plugin template.
- Endpoints: contains the endpoints that are exposed to interact with the plugin or the tool in general. These are defined in the
add_routesfunction available in the plugin template. - Tasks: contains the tasks that are executed when processing files. These tasks are defined in the
bulkfunction available in the plugin template.
Creating a plugin
Section titled “Creating a plugin”As a first step, we must define a functionality and a name for the plugin. In this case, we are going to create a plugin that allows modifying resource titles using the OpenAI API. The name of the plugin will be titleModifier. The steps to create the plugin are described below:
- Create the plugin folder: create a folder with the plugin name in the
pluginsfolder of the application. In this case, the folder will be namedtitleModifier. - Create the plugin file: inside the plugins folder you must always create a
__init__.pyfile. In this case, create the__init__.pyfile inside thetitleModifierfolder as a copy of the plugin template. - Define the plugin logo: the plugin logo should be saved in the
staticfolder inside the plugin folder with the nameimage.png. In this case, save the plugin logo in thetitleModifier/static/image.pngfolder. - Define the plugin dependencies: if the plugin requires additional dependencies, these must be defined in the
requirements.txtfile inside the plugin folder. In this case, the plugin requires theopenailibrary, so create therequirements.txtfile inside thetitleModifierfolder with the following content:
openaiIt is important to always leave a line break at the end of the requirements.txt file to avoid errors in the installation of the dependencies with docker.
-
Define the plugin environment variables: if the plugin requires additional environment variables, these must be defined in an
.envfile in the plugin folder. In this case, the plugin requires theOPENAI_API_KEYvariable with the key generated in the OpenAI account. To do this, open the.envfile in any text editor and assign the generated key. -
Modify the
__init__.pyfile: in the__init__.pyfile the plugin code must be written. To start, the plugin information is modified. This information is located at the end of the__init__.pyfile and must be modified with the following information:
plugin_info = { 'name': 'Plugin para modificar títulos de recursos usando la API de OpenAI', 'description': 'Plugin para modificar títulos de recursos usando la API de OpenAI', 'version': '0.1', 'author': 'BITSOL SAS', 'type': ['bulk'], 'settings': { 'settings_bulk': [ { 'type': 'instructions', 'title': 'Instrucciones', 'text': 'Este plugin permite modificar títulos de recursos usando la API de OpenAI. Para usarlo, selecciona los archivos que quieres modificar y configura las opciones del plugin.', }, { 'type': 'select', 'label': 'Modelo', 'id': 'model', 'default': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'options': [ {'value': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'label': 'GPT 3.5 Turbo'}, {'value': 'gpt-4o', 'label': 'GPT 4o'}, {'value': 'gpt-4o-mini', 'label': 'GPT 4o Mini'}, {'value': 'gpt-4o-turbo', 'label': 'GPT 4o Turbo'} ], 'required': False, }, { 'type': 'text', 'label': 'Instrucciones', 'id': 'instructions', 'default': 'Tengo una herramienta de gestión documental con varios recursos y quiero que me ayudes a reescribir el título de esos recursos para que sean más atractivos y llamen la atención de los usuarios usando pocas palabras. Además, debe estar en español.', 'required': True }, { 'type': 'text', 'label': 'Comando para GPT', 'id': 'input', 'default': 'Por favor, reescribe el siguiente título de un recurso:', 'required': True } ] }}Then you must define the endpoints and tasks of the plugin. To do this, you must modify the add_routes function and the bulk function respectively. In the add_routes function, you must define the endpoints that the plugin will expose for use. By default, the bulk endpoint is already configured for the bulk function call. In this case, the add_routes function must be modified to read as follows:
def add_routes(self): @self.route('/bulk', methods=['POST']) @jwt_required() def process_files(): current_user = get_jwt_identity() body = request.get_json()
if 'post_type' not in body: return {'msg': 'No se especificó el tipo de contenido'}, 400
if not self.has_role('admin', current_user) and not self.has_role('processing', current_user): return {'msg': 'No tiene permisos suficientes'}, 401
task = self.bulk.delay(body, current_user) self.add_task_to_user(task.id, 'titleModifier.bulk', current_user, 'msg')
return {'msg': 'Se agregó la tarea a la fila de procesamientos'}, 201Note that in this case it is validating that the user has permissions to run the plugin. This is important since the plugin is going to modify resource titles and not all users should have access to this functionality. In this case, only users with admin or processing role will be able to execute the plugin.
In addition, the second parameter of the self.add_task_to_user function is the name of the plugin and the function to be executed. This is simply to identify the task in the database and does not affect the operation of the plugin. With this, the bulk function looks like this:
@shared_task(ignore_result=False, name='titleModifier.bulk', queue='low') def bulk(body, user): from openai import OpenAI openai_client = OpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
def modify_title(client, original_title, model, instructions, input): response = client.responses.create( model = model, instructions = instructions, input = input + original_title ) return response.output_text
filters = { 'post_type': body['post_type'] }
if 'parent' in body: if body['parent'] and len(body['resources']) == 0: filters = {'$or': [{'parents.id': body['parent'], 'post_type': body['post_type']}, {'_id': ObjectId(body['parent'])}], **filters}
if 'resources' in body: if body['resources']: if len(body['resources']) > 0: filters = {'_id': {'$in': [ObjectId(resource) for resource in body['resources']]}, **filters}
# obtenemos los recursos resources = list(mongodb.get_all_records('resources', filters, fields={'_id': 1, 'metadata': 1})) if len(resources) == 0: return 'No se encontraron recursos para procesar'
for resource in resources: original_title = resource['metadata']['firstLevel']['title'] new_title = modify_title(openai_client, original_title, body['model'], body['instructions'], body['input']) update = { 'metadata': { 'firstLevel': { 'title': new_title } } } update_data = RecordUpdate(**update) mongodb.update_record('resources', {'_id': resource['_id']}, update_data)
instance = ExtendedPluginClass('titleModifier','', **plugin_info) instance.clear_cache()
return 'ok'Inside the bulk function, the code to be executed when processing the records is defined. In this case, the original title of the resource is obtained and sent to the OpenAI API to be modified. Then, the resource title is updated in the database.
As ArchiHUB’s own functions, there are the mongodb.get_all_records and mongodb.update_record functions. The first function gets the records from the database and the second one updates the record in the database. In addition, at the end of the bulk function, the clear_cache function of the plugin is called to update the changes in the ArchiHUB interface. This is important because if this function is not called, the changes will not be reflected in the ArchiHUB interface unless the cache is regenerated from the application settings.
Processing row
Section titled “Processing row”The plugin runs in a processing queue. This means that when a task is sent to the plugin, it is added to a queue and processed in the background. This is useful to distribute the tasks to different workers and avoid performance problems if everything runs on the same machine and processing queue. In this case, the plugin uses the low queue to process the tasks. For more information on processing queues, see the ArchiHUB documentation.
Frontend interaction fields
Section titled “Frontend interaction fields”For frontend interactions, fields are defined from the plugin_info variable. This variable contains the plugin information and is used to display the information in the ArchiHUB interface. In this case, different field types are being used:
- instructions: used to display an instruction text to the user. This field is not editable and is only shown as information.
- select: is used to display a selection field to the user. In this case, it is being used to select the OpenAI model to be used to modify the title.
- text: is used to display a text field to the user. In this case, it is being used to display the instruction field and the command field for GPT.
Note: in case you require other types of fields, feel free to open an issue in the repository where the ArchiHUB frontend is located. We will be happy to help you implement it. Remember that ArchiHUB is an open source project and we are open to receive contributions from the community.
Plugin repository
Section titled “Plugin repository”To facilitate the understanding of the guide, we have created a repository where you can find the developed plugin. To install it, follow the instructions in the official ArchiHUB documentation.
